A Complete Guide to Bitcoin Transaction Fees
Find the ins and outs of Bitcoin transaction fees: how they're calculated, why they matter, and tips for minimizing costs. A must-read guide.

Bitcoin has provided a decentralized and borderless alternative to traditional currencies. One essential aspect of using Bitcoin is understanding your transaction fee. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the basics of Bitcoin transactions, what transaction fees are, the factors influencing these bitcoin fees, and how you can calculate and reduce them.
Table of Contents
- What Are Bitcoin Transaction Fees?
- Bitcoin Transaction Basics
- Why are Bitcoin transaction fees high?
- The Factors Influencing Transaction Fees
- How to Reduce Bitcoin Transaction Fees
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Bitcoin Transaction Fees?
Transaction fees are small amounts of Bitcoin that users pay to incentivize miners to include their transactions in the next block. These fees are a crucial part of the Bitcoin ecosystem, as they motivate miners to prioritize and validate transactions promptly.
Bitcoin Transaction Basics
Here is a breakdown of the basics of Bitcoin transactions:
How Bitcoin transactions work
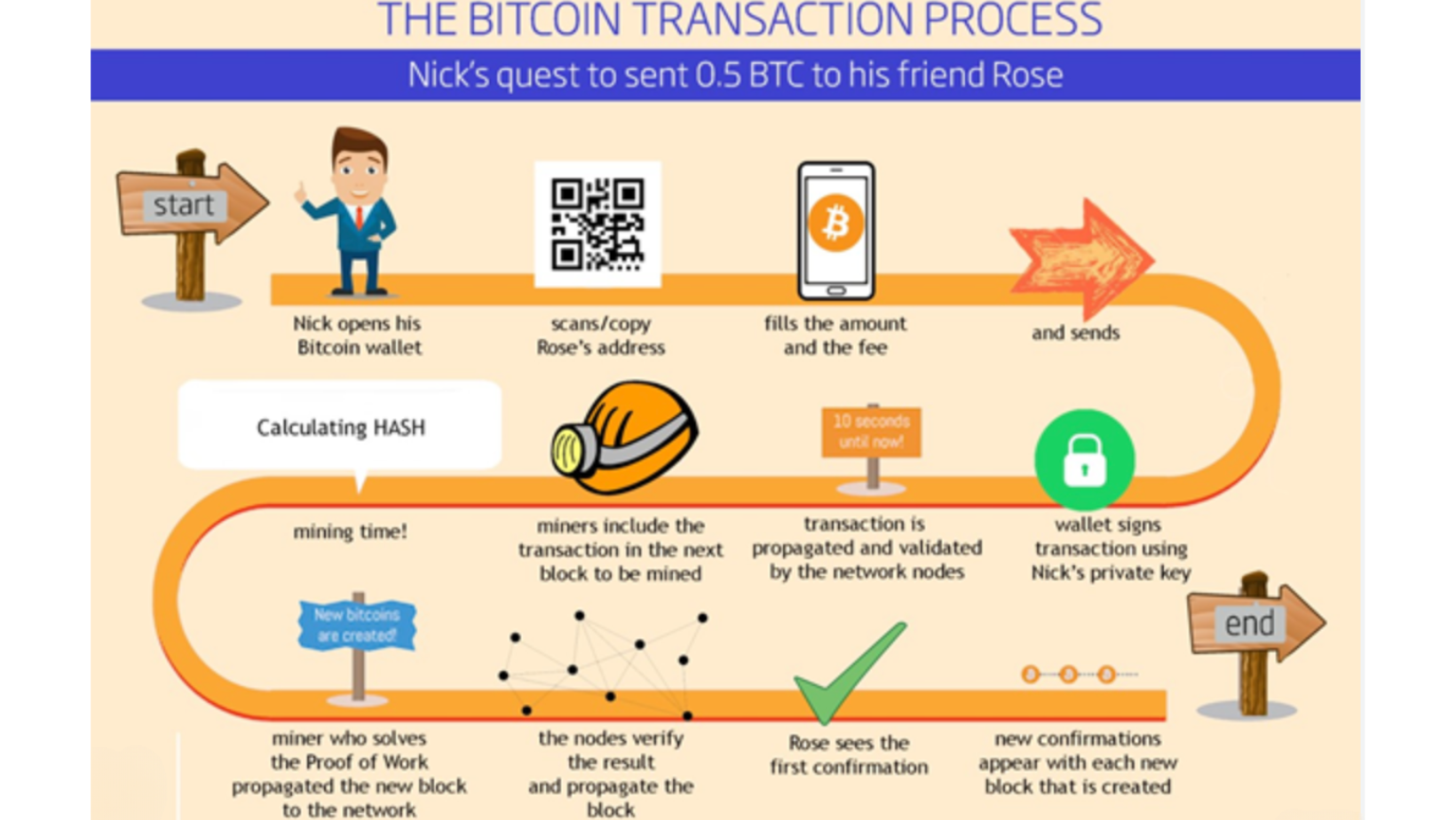
Source: Cryptopolitan
Bitcoin transactions are at the heart of its functionality. When you send Bitcoin to someone, you're essentially creating a digital message that records the transfer of a specific amount from your wallet to the recipient's wallet. This message is then added to a public ledger called the blockchain.
Role of miners in processing Bitcoin transactions
Miners play a vital role in processing and validating Bitcoin transactions. They group transactions into blocks and solve complex mathematical puzzles to add these blocks to the blockchain. In return for their efforts, miners receive rewards in the form of newly created Bitcoin and transaction fees.
Why are Bitcoin transaction fees high?
The high Bitcoin transaction fee has sparked a lot of conversation in the Bitcoin community, especially since a single bitcoin transaction surged to an all-time high of over $37 in December 2023. Let’s look at some of the reasons that cause a spike in Bitcoin transaction fees:
Limited Block Space
Bitcoin blocks have a maximum size limit 1 MB for traditional blocks, though with SegWit it's 4MB, which limits the number of transactions that can be included in each block. This creates a competitive environment where a user bids higher fees to prioritize their transactions over others, especially during times of high demand.
Network Congestion
When many people are sending transactions at the same time, the demand for block space exceeds supply, leading to a backlog of transactions. Users then increase their fees to have their transactions prioritized by miners, who are incentivized to select transactions with higher fees for inclusion in the next block.
Transaction Complexity
Transactions that involve multiple inputs and outputs are larger in size, taking up more block space. Larger transactions require higher fees to be processed promptly. This can happen when consolidating funds from multiple small inputs or splitting a transaction among several recipients.
Mining Economics
Miners prioritize transactions with higher fees because the fees contribute to their revenue, in addition to the block reward. When the block reward decreases over time (halving events), miners' reliance on transaction fees increases, potentially leading to higher fee rates to ensure profitability.
The Factors Influencing Transaction Fees
Below are some of the factors that influence transaction fees:
Bitcoin traffic buildup
Network congestion or traffic buildup occurs when more transactions are waiting to be included in a block than the network can handle. During congested periods, transaction fees tend to rise as users compete to have their transactions processed promptly.
Transaction size
Transaction size depends on several factors, including the number of inputs and outputs. Larger transactions require more data to be processed and, therefore, incur higher fees. Simple transactions with fewer inputs and outputs are generally more cost-effective.
Time of Day and Day of the Week
Transaction fee dynamics can vary depending on the time of day and day of the week. For example, fees might be higher during peak hours when more people are actively using the network. It's essential to consider these factors when planning your transactions.
Type of wallet or exchange in use
Some wallets and exchanges may set default transaction fees that differ from the market rate. Users should be aware of these settings and have the option to customize fees when necessary.
Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO)
Source: Emurgo
A UTXO is essentially a chunk of digital currency that has been sent to a user but not yet spent by them. Each Bitcoin transaction spends previous UTXOs as inputs and creates new UTXOs as outputs, which can then be used in future transactions. This model allows the Bitcoin network to track the ownership of coins without the need for accounts or balances, ensuring security and privacy. The UTXO model affects how much you pay for sending Bitcoin because it's like using many small coins (UTXOs) to make up a payment.
If you have to use a lot of these small coins for one transaction, the transaction becomes larger in size and you end up paying more in fees. Think of it like paying with a huge pile of pennies at a store; it takes more time and effort, so it costs you more. By combining these small coins into fewer, larger ones when the network is not too busy (and fees are low), you can make future transactions simpler and cheaper, similar to exchanging a pile of pennies for a few dollar bills to use later.
How to Reduce Bitcoin Transaction Fees
Here are some ways you can reduce your Bitcoin transaction fees:
Utilize SegWit Addresses

Source: Blockchain Council
SegWit (Segregated Witness) addresses provide an advantage by reducing the size of transactions, which in turn reduces the fee required for a transaction to be confirmed. Using a wallet that supports SegWit addresses (which typically start with "3" or "bc1") can lead to significant savings on fees. Native SegWit wallets, which use addresses starting with "bc1" known as Bech32 addresses, offer lower transaction fees compared to other SegWit addresses, such as legacy and multisig wallets, due to their more efficient use of block space.
Native SegWit addresses remove certain data from the transaction, making these transactions smaller in size. Since Bitcoin transaction fees are calculated based on the size of the transaction in bytes, the reduced size of transactions from Native SegWit addresses means that they require less fee to achieve the same priority as larger transactions.
Opt for Lower Priority
If your transaction is not time-sensitive, you can choose a lower fee rate and wait longer for it to be confirmed. Many wallets provide an option to select the priority level of your transaction; opting for a lower priority can result in lower fees, especially during periods of lower network congestion.
Once you opt for a transaction with low fees, keep in mind that it will take a considerable amount of time before your transaction is confirmed, that is, when the network decongests. If it takes a substantial amount of time before confirmation, your transaction will automatically cancel, which is in about a week or so. To combat your long wait time and avoid cancellation once you opted for a low fee, some wallets offer the option to add more fees to existing transactions to get it confirmed more quickly.
Customize Fee Rates
Some wallets allow users to adjust the fee rate manually. This requires some understanding of the current network conditions to ensure your transaction doesn't end up stuck due to an excessively low fee. Online tools and fee estimators can guide you in setting an appropriate fee. Mempool.io is also a great fee estimator and shows you how congested the network is.
Wallet Features and Coin Selection
Advanced wallets allow a user to prioritize spending older or larger UTXOs to minimize the transaction's byte size, thereby reducing the fee. Coin control can be beneficial for users with wallets containing a mix of small and large UTXOs, enabling them to avoid unnecessary fragmentation and the accumulation of small, unspent outputs that could increase future transaction costs. By choosing which UTXOs to include in a transaction, a bitcoin user can significantly lower their fees, especially during periods of high network congestion when every byte saved can lead to significant savings.
Consolidate Your Inputs
When you control multiple small UTXOs, consider consolidating them into fewer, larger UTXOs during periods of low network congestion. This can be done by sending yourself a transaction when fees are low. Having fewer, larger UTXOs can reduce the size (and thus the fee) of future transactions.
Conclusion
Understanding Bitcoin transaction fees is essential for effectively managing your cryptocurrency transactions. By considering the factors mentioned above, you can make informed decisions to ensure your transactions are optimally priced. Consider using Blockonomics TxFee Score available on the merchant dashboard to determine if your wallet is giving you the best rates for your Bitcoin transactions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I set my transaction fee too low?
If your transaction fee is too low, your transaction may be delayed or remain unconfirmed for an extended period. Eventually, it automatically gets canceled, which is in about a week or so. Miners tend to prioritize transactions with higher fees.
How are transaction fees calculated?
Transaction fees are calculated based on the size of your transaction in bytes and the fee rate (sats/byte) you choose to pay.
Why do we need to pay transaction fees?
Transaction fees incentivize miners to include your transaction in the blockchain and validate it. Without fees, there would be less motivation for miners to prioritize transactions, potentially leading to network congestion.
Do I need to pay a fee for receiving Bitcoin?
No, receiving Bitcoin doesn't involve transaction fees. Transaction fees are typically paid by the sender to ensure the transaction gets processed promptly.
Further Reading
Dynamic Transaction fee wizard
Top 6 Bitcoin Transactions Ever Made in History




Comments ()